In recent years, the dark web has surfaced as a virtual underbelly of the internet, a place where secrecy is paramount and forbidden transactions flourishes. Dark web markets, often known as dark marketplaces, have enthralled both participants and authorities alike with their secretive products, ranging from drugs and hacked information to personal services and arms. The attraction of these markets lies not only in their offerings but also in the lack of central authority of transactions, allowing users to conduct business without conventional supervision.
Yet, the rise of these clandestine platforms has been met with increasing scrutiny and crackdowns from law enforcement agencies worldwide. As authorities become more adept at breaking into and destroying these operations, the landscape of dark web trade is in continual evolution. This interaction between innovation and regulation defines the path of the underworld bazaar, where fresh marketplaces rise from the ashes of past marketplaces, and the rhythm of hidden transactions and transparency continues to shape the underground web.
Foundations of the Dark Web
The origins of the deep web can be traced back to the early days of the internet when privacy and anonymity were paramount issues for developers and internet participants alike. In the mid-1990s, the U.S. Naval Research Laboratory created the Tor initiative to enable safe interactions for government organizations. Tor, which represents The Onion Router, was developed to protect the persons and locations of its users by routing internet traffic through multiple servers and encrypting data at each stage.
As the technology matured, the possibilities for the deep web expanded. By the 2000s, individuals began to leverage Tor for other safe interactions. It became a refuge for those wishing to talk about sensitive topics without worry of surveillance and censorship. This led to the emergence of multiple platforms and forums where users could engage in secrecy. The appeal of privacy drew a wide crowd, from protesters and journalists to individuals looking for a method to participate in forbidden practices.
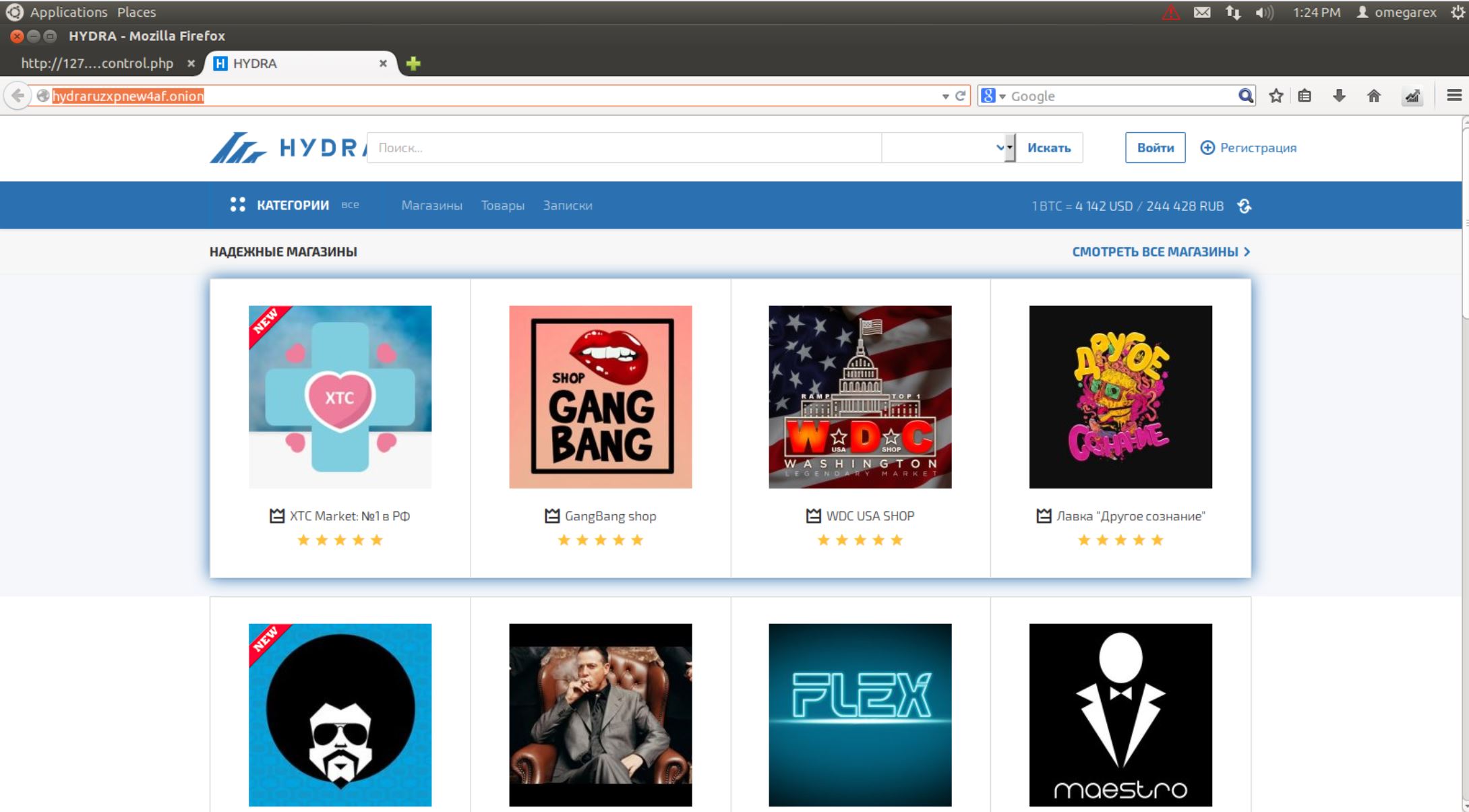
By the end of the 2000s, dark web marketplaces began to flourish. These online hubs offered a range of goods and services, from illegal narcotics to cybersecurity tools. The use of cryptocurrencies for exchanges further facilitated this underground trade, as it provided additional layers secrecy. As dark web markets gained attention, they became a focal point for authorities, igniting a cat-and-mouse game that persists to this day.
Key Players in Darknet Marketplaces
The landscape of dark web marketplaces is shaped by various important participants who play a role its special ecosystem. Vendors are often seasoned dealers who concentrate in particular products, ranging from illicit drugs to counterfeit items. They utilize secure communication and disguise to protect their profiles while navigating the intricacies of darknet transactions. Some sellers establish a presence through user ratings, which can substantially impact their ability to attract buyers and sustain a profitable operation.
Consumers in darknet markets are likewise motivated by multiple reasons, including access to goods that may be illegal or hard to find in conventional markets. These people are commonly tech-savvy and recognize the importance of maintaining anonymity, often using crypto assets to carry out transactions. Some clients are risk-taking patrons seeking novelty, while others are determined, drawn to the temptation of acquiring controlled substances or other illegal items without the threat of discovery in the real world.
Market administrators and moderators play a key role in maintaining the operation of these platforms. They manage operations, impose rules, and ensure that transactions move forward seamlessly. Many sites also feature support services, such as dispute resolution and trust services, designed to safeguard both consumers and merchants. This threefold of players creates a vibrant environment where credibility and security are paramount, despite the built-in risks involved in the black market.

The Decrease of Dark Web Trade
The decrease of trade on the dark web can be linked to increased law enforcement actions targeting illegal activities. Governments around the world have become more skilled at tracking and charging individuals involved in transactions on the dark web. Crackdowns like Silk Road marketplace and AlphaBay marketplace led to major captures, which created a chilling effect on both vendors and buyers. As the risks of participating in dark web markets increased, many users started to reevaluate their participation in these illicit platforms.
Another factor contributing to the decrease is the rise of new solutions for accessing illegal goods and products. The dark web was once viewed as the main avenue for such deals, but developments in technology have led to the emergence of readily available black markets on the clearnet. This change has drawn many users away from the anonymity and hazards associated with dark web markets, opting for more accessible and viewed less risky options. dark markets
Finally, the general market saturation has contributed in the decrease of dark web trade. As many emerging platforms emerged, rivalry increased among sellers, often leading to a decrease in product quality and reliability. Consumers began to diminish confidence in the distributed market, realizing that the assured anonymity did not always guarantee security or quality. Combined with the tightening of law enforcement and the arrival of alternative methods, the dark web trade has seen a marked downturn in user engagement and transaction volume.
